TYM2019
Hideki Tanaka, Takuma Yagasaki, and Masakazu Matsumoto
On the role of intermolecular vibrational motions for ice polymorphs I: Volumetric properties of crystalline and amorphous ices
J. Chem. Phys. 151, 114501 (2019).
Nominated as Editor’s pick of the journal.
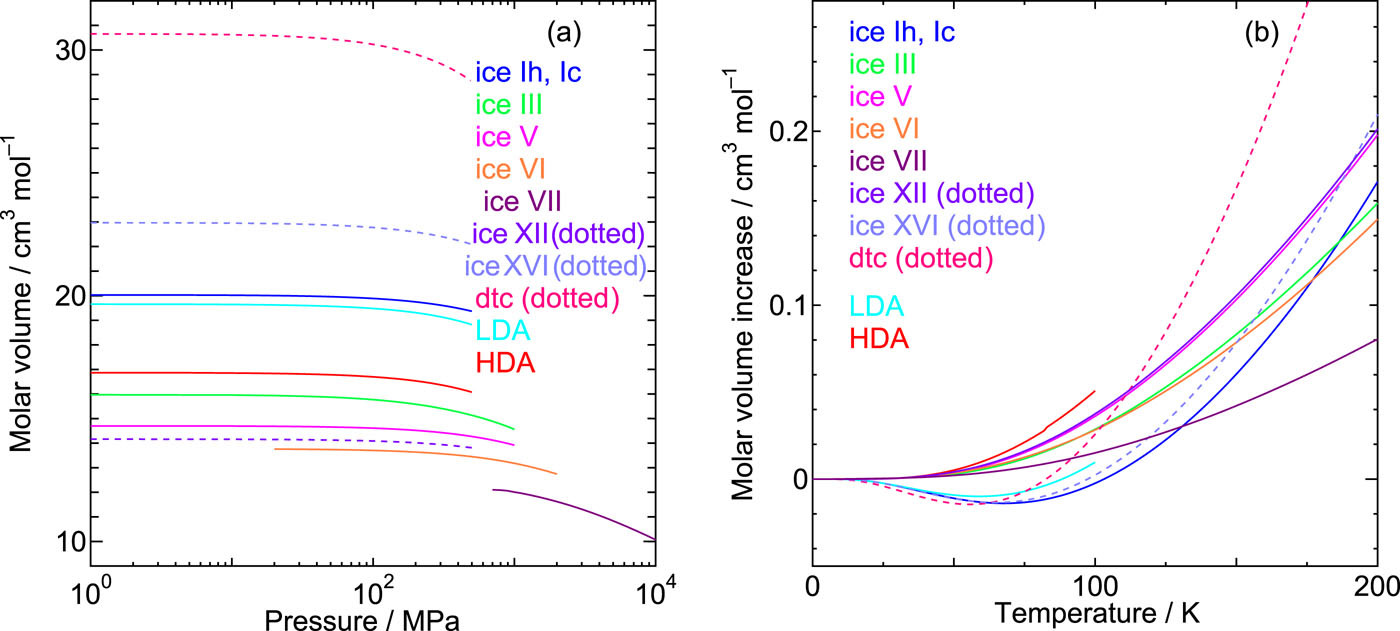
Intermolecular vibrations and volumetric properties are investigated using the quasiharmonic approximation with the TIP4P/2005, TIP4P/Ice, and SPC/E potential models for most of the known crystalline and amorphous ice forms that have hydrogen-disordering. The ice forms examined here cover low pressure ices (hexagonal and cubic ice I, XVI, and hypothetical dtc ice), medium pressure ices (III, IV, V, VI, XII, hydrogen-disordered variant of ice II), and high pressure ice (VII) as well as the low density and the high density amorphous forms. We focus on the thermal expansivities and the isothermal compressibilities in the low temperature regime over a wide range of pressures calculated via the intermolecular vibrational free energies. Negative thermal expansivity appears only in the low pressure ice forms. The sign of the thermal expansivity is elucidated in terms of the mode Grüneisen parameters of the low frequency intermolecular vibrational motions. Although the band structure for the low frequency region of the vibrational density of state in the medium pressure ice has a close resemblance to that in the low pressure ice, its response against volume variation is opposite. We reveal that the mixing of translational and rotational motions in the low frequency modes plays a crucial role in the appearance of the negative thermal expansivity in the low pressure ice forms. The medium pressure ices can be further divided into two groups in terms of the hydrogen-bond network flexibility, which is manifested in the properties on the molecular rearrangement against volume variation, notably the isothermal compressibility.
水素無秩序化を有するほとんどの既知の結晶及び非晶質氷形状に対して,TIP4P/2005,TIP4P/Ice及びSPC/Eポテンシャルモデルによる準調和近似を用いて分子間振動及び体積特性を調べた。ここで調べた氷の形は,低圧氷(六角形と立方体の氷I、XVI、および仮想のdtc氷),中圧氷(氷IIのIII、IV、V、VI、XII、水素無秩序型),高圧氷(VII)と同様に,低密度と高密度の非晶質形を含む。分子間振動自由エネルギーにより計算した広い圧力範囲にわたる低温領域における熱膨張率と等温圧縮性に焦点を当てた。負の熱膨張率は低圧氷形でのみ現れた。熱膨張率の符号を低周波分子間振動運動のモードGrüneisenパラメータにより解明した。中圧氷の振動状態密度の低周波領域に対するバンド構造は低圧氷のそれと非常に似ているが,体積変化に対する応答は逆である。低周波モードにおける並進運動と回転運動の混合が,低圧氷形態における負の熱膨張率の出現に重要な役割を果たすことを明らかにした。中圧氷は水素結合ネットワークの柔軟性の観点からさらに2つのグループに分けることができ,これは体積変化に対する分子再配列の特性,特に等温圧縮性に現れる。(ミライ翻訳による機械翻訳)
research papers paper2019 water ice clathratehydrate