TYM2020B
Tanaka, H, Yagasaki, T, Matsumoto, M.
Cage occupancy and dissociation enthalpy of hydrocarbon hydrates.
AIChE J. 2020;e17009.
First Published: 2020-08-05
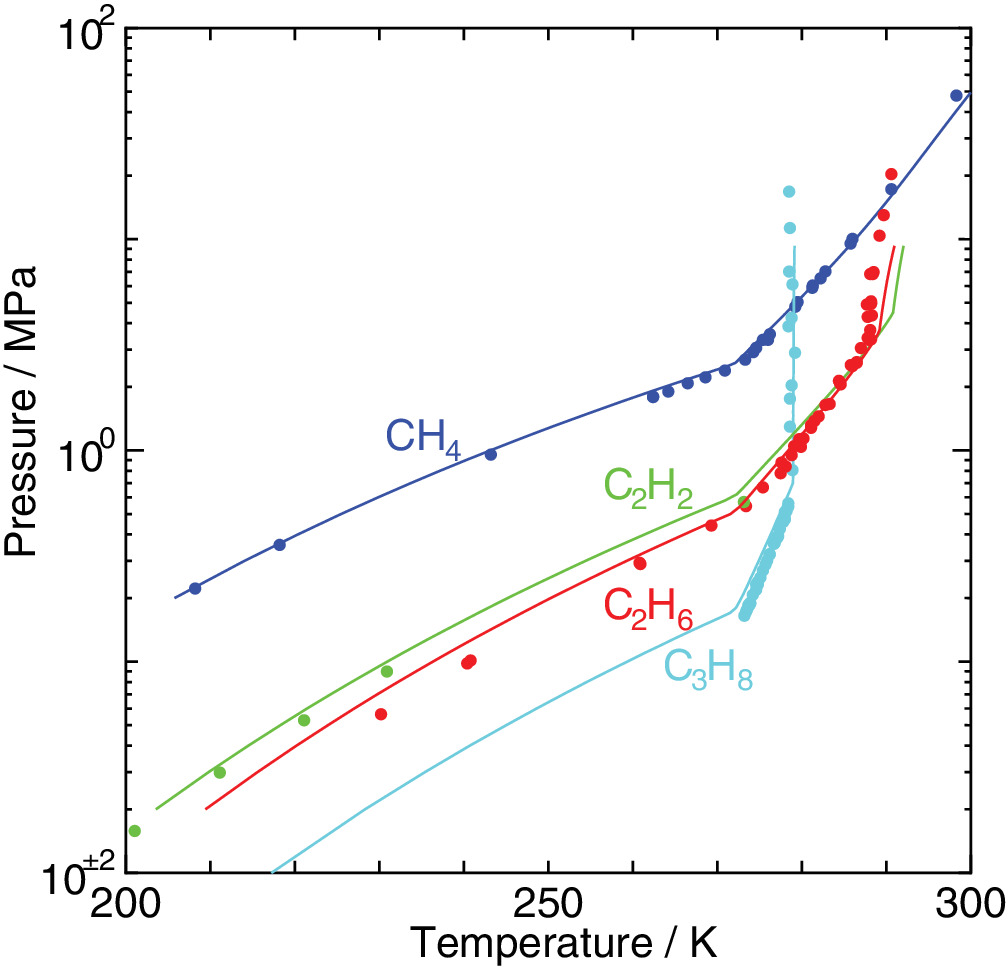
An elaborated statistical mechanical theory on clathrate hydrates is applied to exploration of their phase equilibria and dissociation enthalpies. The experimental dissociation pressures of methane, ethane, acetylene, and propane hydrates are well recovered by the method we have proposed. We estimate water/hydrate and hydrate/guest two‐phase coexisting conditions in the temperature, pressure, and composition space in addition to three‐phase equilibrium conditions. It is shown that the occupancy of guest molecules and the two‐phase boundaries in the phase diagram vary depending sensitively on its size. Enthalpy components arising from the host and guest interactions are separately calculated from the temperature dependence of the corresponding free energy values. This enables to evaluate the dissociation enthalpy at any stable and metastable thermodynamic state taking account of the phase transition in the coexisting phase such as melting of ice, notably that along the three‐phase equilibrium line.
本研究では、クラスレート水和物の相平衡と解離エンタルピーを調べるために、クラスレート水和物の精緻な統計力学的理論を適用した。メタン,エタン,アセチレン,プロパン水和物の実験的な解離圧力は、私たちが提案した方法で十分に回復した。三相平衡条件に加えて、温度・圧力・組成空間における水/水和物及び水和物/ゲストの二相共存条件を推定した。その結果、相図中のゲスト分子の占有率と二相境界が、その大きさによって敏感に変化することが示された。ホスト分子とゲスト分子の相互作用から生じるエンタルピー成分を、対応する自由エネルギー値の温度依存性から個別に計算した。これにより、氷の融解のような共存相の相転移、特に三相平衡線に沿った相転移を考慮して、安定で準安定な熱力学状態での解離エンタルピーを評価することができる。 (DeepLによる機械翻訳)
research papers paper2020 water ice clathratehydrate